By Christopher Budd, Cybersecurity Evangelist
The January 2026 Patch Tuesday release is most notable for what happened AFTER Patch Tuesday. Specifically, on January 26, 2026, Microsoft released CVE-2026-21509 – Microsoft Office Security Feature Bypass Vulnerability out-of-band.
As a reminder, an “out-of-band” release from Microsoft means that they view the threat environment around the vulnerability being addressed as being significant enough to warrant the risk of an out-of-process release by them and by their customers. We talk about CVE-2026-21509 in more detail below, but if you haven’t already deployed this patch, please do so as quickly as possible.
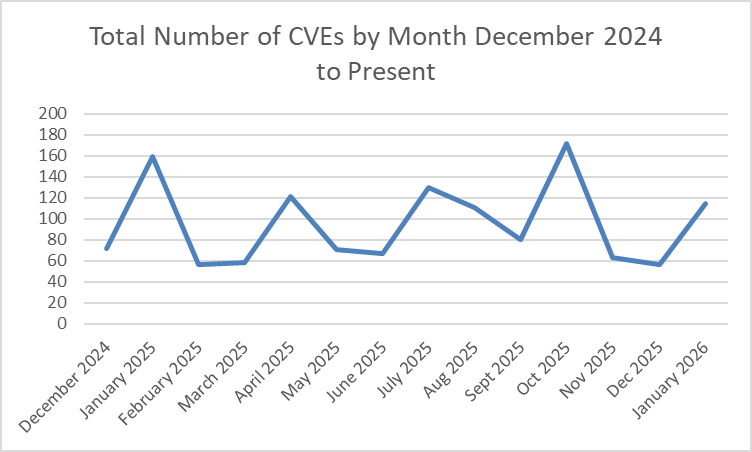
Otherwise, the January release is a more moderate release in terms of the quantity of CVEs addressed. Coming after two lighter months in November and December 2025, it’s consistent with patterns of heavier months coming after lighter ones. But it’s notable for not being as heavy a month as October 2025.
You can also see below that this release is not as heavy as January 2025.
We look at the January 2026 Patch Tuesday to highlight information of greatest importance for threat hunters and defenders focused on vulnerability management and attack prevention.
I examine the vulnerabilities that I have defined as “notable” using the criteria below.
This criteria is based on my experience building and leading Patch Tuesday for Microsoft and other companies in the industry. They are the markers for vulnerabilities that are most likely to be used in attacks against unpatched systems and of greatest interest and concern for defenders.
In decreasing order of priority based on information Microsoft provided at the time of release, January 13th, 2026 and January 26th, 2026 for the out-of-band fix:
- Those that are known by Microsoft to be exploited
- Those that are known by Microsoft to be publicly disclosed
- Those with a “Severity Rating” of “Critical”
- Those with an “Exploitability Assessment” of “More Likely”
For each of the vulnerabilities that meet these criteria below, I provide some information on the technology and information about the threat environment around that vulnerability as of this writing.
Vulnerabilities that are not “notable” are not covered. This is to help defenders focus on the most impactful threats in this month’s release. However, remember that the threat environment evolves; things that on paper appear as not “notable” at time of release, can later be under attack. Ultimately, you should deploy all appropriate updates.
The information in this article is intended to help you understand and better prioritize vulnerabilities for remediation in your environment.
In Appendix A, you will find the complete listing of this month’s Microsoft bulletins with hyperlinks to information about the individual vulnerabilities on the MSRC website.
Top Level Findings
Numbers of CVEs: Total, Critical/Important Severities, and Notable
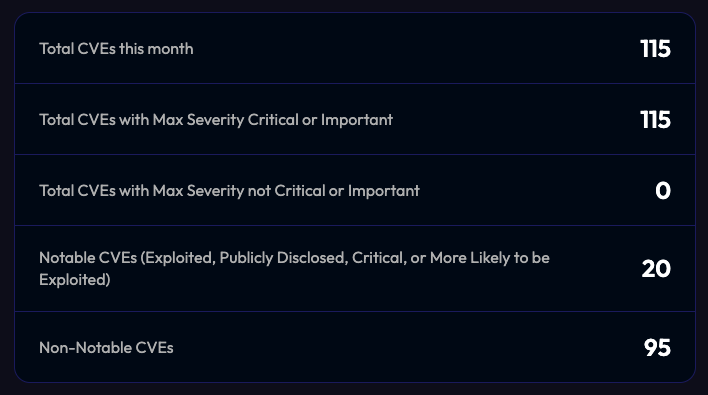
Threat Environment and Exploit Information

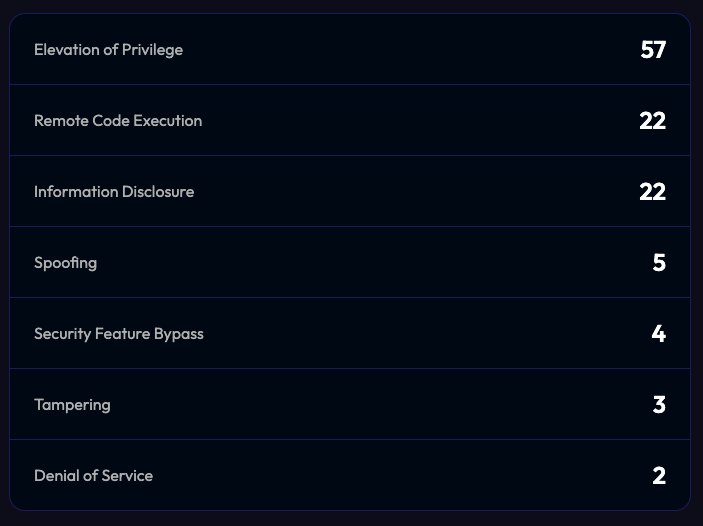
Vulnerability Impacts
Notable CVEs
Exploited
CVE-2026-21509 – Microsoft Office Security Feature Bypass Vulnerability
Like we noted above, this is the top priority for January’s releases, even though it was only released on January 26, 2026.
Public reports from Bleeping Computer published February 2, 2026 on CVE-2026-21509 indicate that CERT-UA, the Ukrainian Computer Emergency Response Team (CERT), has observed and reported in-the-wild attacks against this vulnerability.
The vulnerability is listed as a “security feature bypass” by Microsoft. The executive summary notes that “Reliance on untrusted inputs in a security decision in Microsoft Office allows an unauthorized attacker to bypass a security feature locally”. The FAQ for the vulnerability says “An attacker must send a user a malicious Office file and convince them to open it.”
Based on the published information about the vulnerability and my time writing security bulletins like these for Microsoft, it is reasonable to postulate the attack scenario. Attackers craft Office documents designed to run malicious code and are specially malformed to suppress the security warnings normally raised when documents like this are opened as attachments. Attackers then send these documents as attachments in email, typically in highly targeted attacks. Once the attachment is opened and the attacker’s code has executed, the attacker’s malicious code is on the system and ready for the next steps in the attack. Frequently, we see tactics like this used in espionage-type attacks focused on gathering information from the targets.
The Ukrainian CERT advisory bears out this type of attack. As of this writing, no English version of the advisory is available. A Claude translation of the Ukrainian advisory, cross-checked and verified with ChatGPT, documents the following attack chain:
- Document opens → WebDAV connection to external resource
- Downloads shortcut file with malicious code
- Deploys: DLL (“EhStoreShell.dll”), shellcode image (“SplashScreen.png”), COM hijacking registry mod, scheduled task (“OneDriveHealth”)
- Terminates/restarts explorer.exe → loads DLL → executes shellcode → deploys COVENANT framework
- C2 via legitimate Filen cloud storage (filen.io)
The Ukrainian report indicates that they’ve seen only a small number of attacks, what at Microsoft we would call ‘limited and targeted’. They attribute these attacks to APT28, the group best known for their work behind the Hillary Clinton email attack in 2016.
A review of the Flare Platform for information around this vulnerability shows no information about the attacks until after the release of the CERT-UA advisory, and no discussions other than dark web and Telegram news postings about the vulnerability. This is consistent with the discovery and early use of a vulnerability like this by a threat actor group like APT28.
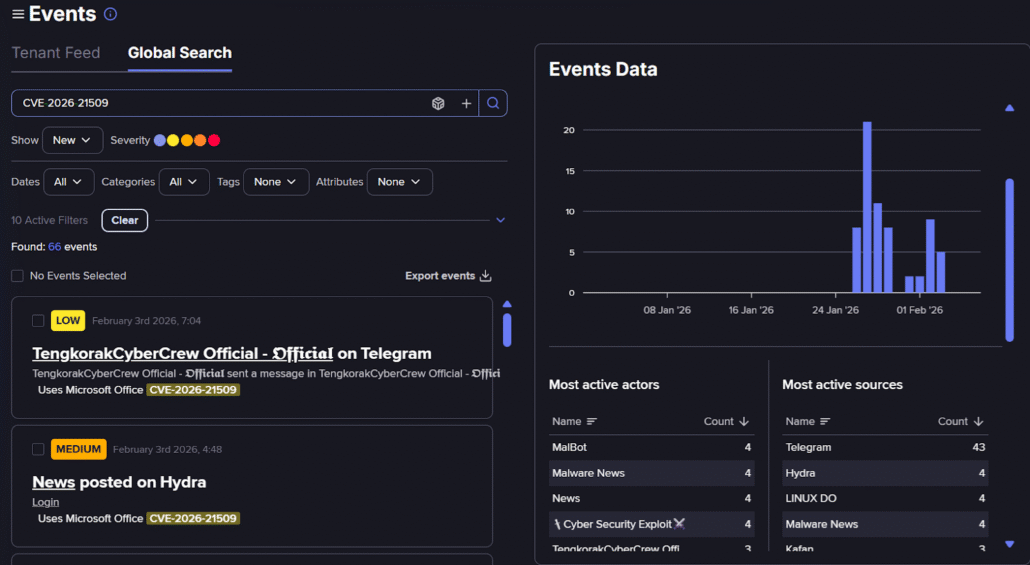
Flare search on CVE-2026-21509 (Flare link, sign up for the free trial to access if you aren’t already a customer)
While this vulnerability appears to be contained to the “limited and targeted” threat category for now, we regularly see vulnerabilities like this “trickle down” into cybercrime and more general usage quickly. As a result, it makes sense to make this a top priority in your patching.
CVE-2026-20805 – Desktop Window Manager Information Disclosure Vulnerability
At the time of release, CVE-2026-20805 was called out at the top of the list of vulnerabilities of concern because it was the only vulnerability listed as “exploited” at that time.
The vulnerability is rated as “Important” by Microsoft, with a CVSS base score of 5.5. It’s an information disclosure vulnerability, and Microsoft notes in the FAQ “The type of information that could be disclosed if an attacker successfully exploited this vulnerability is a section address from a remote ALPC port which is user-mode memory.”
ALPC is an “asynchronous” or “advanced” local procedure call (LPC). It’s a form of interprocess communications within the Windows platform that goes back to the earliest days.
How the vulnerability can be useful to attackers is summed up by Dustin Childs at Trend Micro’s Zero Day Initiative in his write-up: “This bug allows an attacker to leak a section address from a remote ALPC port. Presumably, threat actors would then use the address in the next stage of their exploit chain – probably gaining arbitrary code execution.”
This indicates to us that this is a vulnerability that has little use on its own but can be useful as part of an attack chain, which is important information in assessing overall risk for prioritizing patches.
Another important, practical factor in prioritizing security patches is understanding the actual threat environment and how widespread exploitation or the risk of it is.
At the time of release, Microsoft noted that this vulnerability was “Exploited.” But as ZDI’s Childs notes in his write-up “Microsoft offers no indication of how widespread these exploits may be, but considering the source, they are likely limited.”
One way to estimate “how widespread these exploits may be” is to look at the “Acknowledgements” for the vulnerability in the Microsoft write-up. This lists “Microsoft Threat Intelligence Center and Microsoft Security Response Center.” This tells you that while this vulnerability is publicly “exploited,” that exploitation was found by Microsoft, not someone outside of Microsoft. Microsoft does not release exploit code for vulnerabilities publicly as a matter of policy. Based on this, we can infer that public exploit information for this vulnerability at the time of release was very limited, possibly known only to the attackers and Microsoft.
A search of the open web for “CVE-2026-20805 exploit” on Google, Bing, DuckDuckGo, Reddit, Mastodon (infosec.exchange instance), GitHub and Bluesky shows very little information on this vulnerability beyond announcing its release. We don’t see first-hand reports of active exploits and only a couple of detailed analyses of the vulnerability by Alon Barad on CVEreports, and Penligent’s Hacking Labs.
The lack of any major indications of activity around this vulnerability on the open web gives us an indication that, as Childs notes, the exploits may indeed be limited.
Fortunately, we have the ability to augment this public information with additional intelligence from the dark web and Telegram from Flare as shown below.
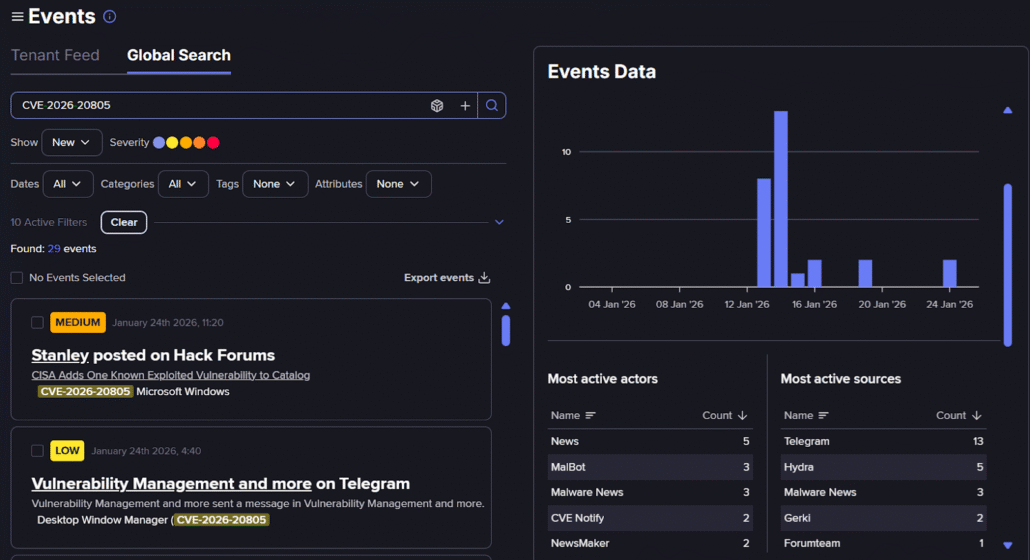
Flare search on CVE-2026-20805 (Flare link, sign up for the free trial to access if you aren’t already a customer)
This shows us a spike in news postings about the vulnerability around release day, a couple of random mentions since then, and nothing at all since January 24, 2026.
Taking all of the information we’ve outlined together, we can form a more practical threat environment assessment on our own to supplement the release day information from Microsoft.
This vulnerability was known to be exploited at time of release. But since then there is no evidence of further exploitation or movement around this vulnerability.
The vulnerability itself is rated as “Important.” But it most likely can be useful only in the context of other vulnerabilities as part of a chained attack.
This gives us a more complex and nuanced picture for your risk assessment. This isn’t just an “exploited at release time” vulnerability. It’s an “exploited at release time with very little additional activity since then that we can find” vulnerability.
Publicly Disclosed
CVE-2023-31096 – MITRE: CVE-2023-31096 Windows Agere Soft Modem Driver Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability
This patch addresses a vulnerability that was discovered originally in 2023 affecting the Agere Soft Modem Driver that ships with Windows.
There’s very little information available about this vulnerability, even after three years of being in the public space.
Most importantly, there’s no indication that this has ever been attacked.
A search on Flare, in fact, shows that throughout its lifetime, this vulnerability has only been mentioned eight times ever throughout its history, and those mentions are in the context of the January 2026 Patch Tuesday release. You can see this below, where the “Event Data” is set to “All Time.”
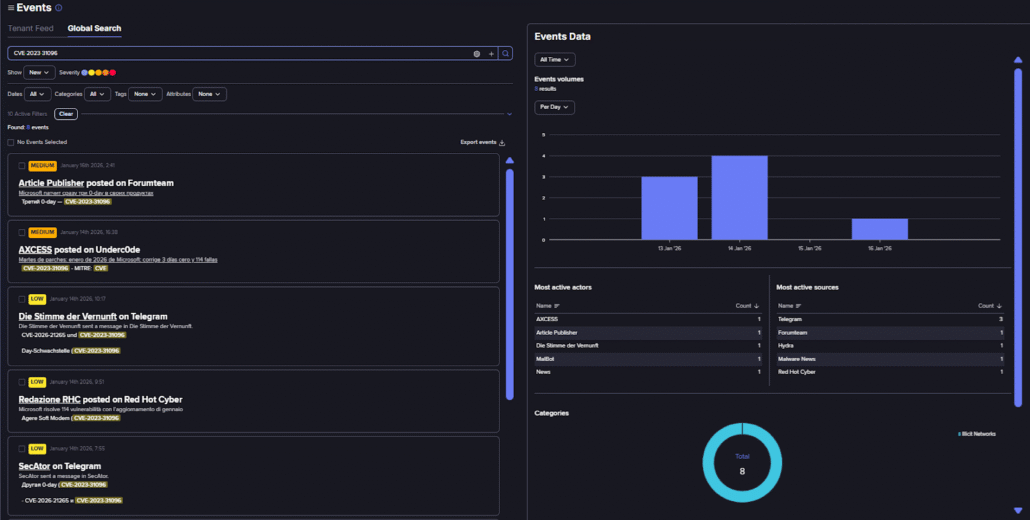
Flare search on CVE-2023-31096 (Flare link, sign up for the free trial to access if you aren’t already a customer)
Even though this vulnerability is publicly known and has been for three years, you can factor this knowledge of the threat environment into your risk assessment and prioritize this appropriately.
CVE-2026-21265 – Secure Boot Certificate Expiration Security Feature Bypass Vulnerability
This vulnerability can be somewhat misleading in its title and labeling.
This CVE is for ensuring that the digital certificates that underpin Windows Secure Boot are updated before they expire. If those digital certificates expire, then the Windows system’s ability to receive security updates is harmed.
This issue is “public” because Microsoft has been warning about it for several months now through this knowledge base (KB) article 5062710.
This is a very important update to apply. But from a threat assessment point of view, there’s almost no attack vector exposed by this.
This is backed up by a search in Flare which shows only minimal, automated mention of this vulnerability on news recaps. (No screenshot included for this reason.)
Criticals
CVE-2026-20944 – Microsoft Word Remote Code Execution Vulnerability, CVE-2026-20952 – Microsoft Office Remote Code Execution Vulnerability, CVE-2026-20953 – Microsoft Office Remote Code Execution Vulnerability, CVE-2026-20955 – Microsoft Excel Remote Code Execution Vulnerability, CVE-2026-20957 – Microsoft Excel Remote Code Execution Vulnerability
These five critical Office vulnerabilities can be treated as a single clutch.
All five of these are memory-related vulnerabilities. They are all rated critical because of the risk of code execution from maliciously formed Office files, much like we discussed earlier in regard to CVE-2026-21509. “The close proximity of the CVE numbers suggests these vulnerabilities are connected or share common characteristics.” t
It is worth noting that three of the five deserve more attention because they have a preview pane attack vector. This means that they can be exploited when a malicious email message is rendered in Outlook using the preview pane with no direct interaction. The three affected are:
- CVE-2026-20944 – Microsoft Word Remote Code Execution Vulnerability
- CVE-2026-20952 – Microsoft Office Remote Code Execution Vulnerability
- CVE-2026-20953 – Microsoft Office Remote Code Execution Vulnerability
None of these vulnerabilities were under active attack or publicly known at the time of release. A review of Flare shows no major discussions or activity around these vulnerabilities, though it is worth noting that CVE-2026-20952 is showing up slightly more than the other four vulnerabilities.
As with all “critical” Office vulnerabilities like this, any limits on the user’s account would limit the attacker’s actions. If users are running as administrators, however, this presents no effective mitigation.
CVE-2026-20822 – Windows Graphics Component Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability
This is an elevation of privilege vulnerability that can be used by attackers to gain SYSTEM-level control. This vulnerability is the result of a race condition affecting the processing of graphics files.
One thing worth noting from Microsoft is: “In a GPU paravirtualization scenario, an attacker who successfully exploited this vulnerability could traverse the guest’s security boundary to gain access to the host environment.” That makes this vulnerability of particular concern for GPU paravirtualization scenarios.
It’s worth noting that while “critical” in severity, this vulnerability is assessed as “exploitation less likely.”
There’s minimal chatter about this vulnerability in the cybercrime ecosystem.
CVE-2026-20854 – Windows Local Security Authority Subsystem Service (LSASS) Remote Code Execution Vulnerability
This vulnerability can enable an attacker to execute code locally in the SYSTEM-level security context. It occurs as a result of a use after free condition within the Local Security Authority Subsystem Service (LSASS).
It’s worth noting that this also is rated as “critical” but also with “exploitation less likely.”
There’s minimal chatter about this vulnerability in the cybercrime ecosystem.
CVE-2026-20876 – Windows Virtualization-Based Security (VBS) Enclave Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability
This is another local vulnerability: an attacker would have to run code on the vulnerable system to exploit this vulnerability. This is also an elevation of privilege (EoP) vulnerability, meaning that an attacker could use it to elevate to administrative privileges, making it more likely to be used in conjunction with other vulnerabilities rather than alone.
It’s also worth noting that this too is rated as “critical” but also with “exploitation less likely.” And once again, there’s minimal chatter about this vulnerability in the cybercrime ecosystem.
Exploitability More Likely
CVE-2026-20922 – Windows NTFS Remote Code Execution Vulnerability, CVE-2026-20840 – Windows NTFS Remote Code Execution Vulnerability
CVE-2026-20843 – Windows Routing and Remote Access Service (RRAS) Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability
CVE-2026-20871 – Desktop Windows Manager Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability
CVE-2026-20860 – Windows Ancillary Function Driver for WinSock Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability
CVE-2026-20820 – Windows Common Log File System Driver Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability
CVE-2026-20817– Windows Error Reporting Service Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability
CVE-2026-20816 – Windows Installer Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability
This month there are eight “Important” and “Exploitation More Likely” vulnerabilities that are not “exploited” or “publicly disclosed.” All eight affect Microsoft Windows. Two of these vulnerabilities are remote code execution, and the remaining six are elevation of privilege (EoP).
For those interested in more details on the code execution vulnerabilities which both affect Windows NTFS, Pietro Melillo has a good write-up which also includes information on how attackers could seek to exploit these vulnerabilities.
Beyond that write-up, however, there is no more movement towards exploits or attack code against any of these.
Multiple Vulnerability Clusters
Often it is helpful to see when similar vulnerabilities being addressed occur around specific products, technologies or features. The table below shows this month’s occurrences of multiple vulnerability clusters.
Appendix A: January 2026 Microsoft CVEs
Below is the complete list of CVEs released this month. This data is taken from the Microsoft Security Response Center (MSRC) Security Update Guide and contains all CVEs that were released on January 13, 2026 and the out-of-band fix from January 26, 2026. It does not contain any third-party or Chromium (Microsoft Edge) vulnerabilities.
The data below has been grouped and sorted as follows:
- All where Exploited = Yes
- All where Publicly Disclosed = Yes
- All where Severity = Critical
- All where Exploitation = More Likely, sorted by decreasing severity, sorted alphabetically by impact
- All where Exploitation = Less Likely, sorted by decreasing severity, sorted alphabetically by impact
- All where Exploitation = Unlikely, sorted by decreasing severity, sorted alphabetically by impact
- Any remaining items
Monitor for Emerging Threats with Flare
Flare helps security practitioners stay ahead of newly disclosed CVEs by continuously monitoring the clear and dark web and threat actor communities for early signals of exploitation. Flare’s collection includes more than 50,000 cybercrime Telegram channels, hundreds of cybercrime forums, ransomware leak sites, and dark web marketplaces, in addition to one of the most comprehensive sets of breached identity data in the industry.
See what external threats are exposed for your organization by signing up for our free trial.