This article was updated on December 14th, 2025.
Leaked credentials on the dark web come in many forms, each with varying degrees of risk. Credential stuffing has become one of the primary ways threat actors take over both consumer and enterprise accounts in the 2020s. Credentials are easy to use, require little technical sophistication, and allow attackers to automate account takeover at scale.
Detect and Remediate Leaked Credentials Automatically
Flare continuously monitors stealer logs, combolists, ULPs, and breach databases for your exposed credentials. When we detect a match, our Entra ID integration automatically triggers password resets before attackers can act.
We explore combolists and the different types of leaked credentials available to threat actors on the dark web and Telegram. Detecting and rapidly remediating exposed credentials is one of the most critical security activities for enterprises in 2026 and beyond.
Breaches from Snowflake’s customers to Change Healthcare were a direct result of threat actors simply plugging already-available credentials into sensitive enterprise systems.
What are the Types of Leaked Credentials?
Nomenclature here can be a little bit difficult, simply because the ecosystem is complex. Fundamentally leaked credentials are a username/password pair that are being traded or distributed in the cybercrime ecosystem.
Leaked credentials can come from a number of places. They can come from a named breach, in which a company leaks the usernames and passwords for all their users, or they can come from a stealer log, where one user leaks all of the credentials saved in the browser. Check out the infographic below for a visual explanation:
Understanding Leaked Credentials
Not all leaked credentials are equal. Here’s how stealer logs, ULPs, and combolists differ and why it matters for your security posture.
Complete data packages harvested directly from infected devices. Stealer logs contain far more than just credentials. They include active session cookies, browser autofill data, system fingerprints, and saved payment information. This allows attackers to bypass MFA entirely by hijacking authenticated sessions.
Credentials paired with the specific URL they belong to. The URL context makes these highly actionable for attackers since they know exactly which service to target. Often extracted from stealer logs with session data stripped out, or parsed from structured breach dumps.
Simple email:password or username:password pairs with no URL context. These are used in large-scale credential stuffing attacks where attackers spray credentials across thousands of services hoping for password reuse. Often contain millions of entries aggregated from multiple sources.
Broad category covering any exposed username/password pair. May come from traditional data breaches (like LinkedIn or Adobe), phishing campaigns, or accidental public exposure. Risk level depends heavily on age, whether passwords are hashed, and password reuse patterns.
How They Relate
Each transformation loses context and risk decreases accordingly. A stealer log with fresh session cookies enables immediate account takeover. The same credential in a combolist requires the attacker to guess which services it works on. This is why detecting credentials at the stealer log stage is critical. You stop the attack before session hijacking can occur.
What is a Combolist?
A combolist is a collection of username and password pairs formatted for credential stuffing attacks. Unlike raw breach dumps, combolists are curated specifically for offensive use. They strip away unnecessary data and organize credentials in standardized formats that automated attack tools can ingest directly.
Why Do Threat Actors Use Combolists?
Combolists exploit a simple reality: people reuse passwords. When credentials from one breach are tested against hundreds of other services, attackers reliably gain access to accounts that share the same password. This technique, called credential stuffing, requires minimal technical skill and scales easily.
Where Do the Credentials for Combolists Come From?
Threat actors aggregate credentials from multiple sources including data breaches, stealer logs, and phishing campaigns. The raw data is de-duplicated, cleaned, and formatted into simple text files. There is no universal standard. Some combolists use plaintext passwords while others contain hashes. Many are organized by geography, industry, or email domain to increase relevance for targeted attacks.
What Makes Combolists Valuable?
Not all combolists are equal. Threat actors evaluate them based on three factors:
- Recency: Fresh credentials are more likely to still be valid
- Exclusivity: Lists that have not been widely shared command premium prices
- Targeting: Credentials tied to high-value services (corporate SSO, banking, cloud infrastructure) are worth more than consumer accounts
The most dangerous combolists combine all three: recently harvested, privately held, and focused on enterprise targets.
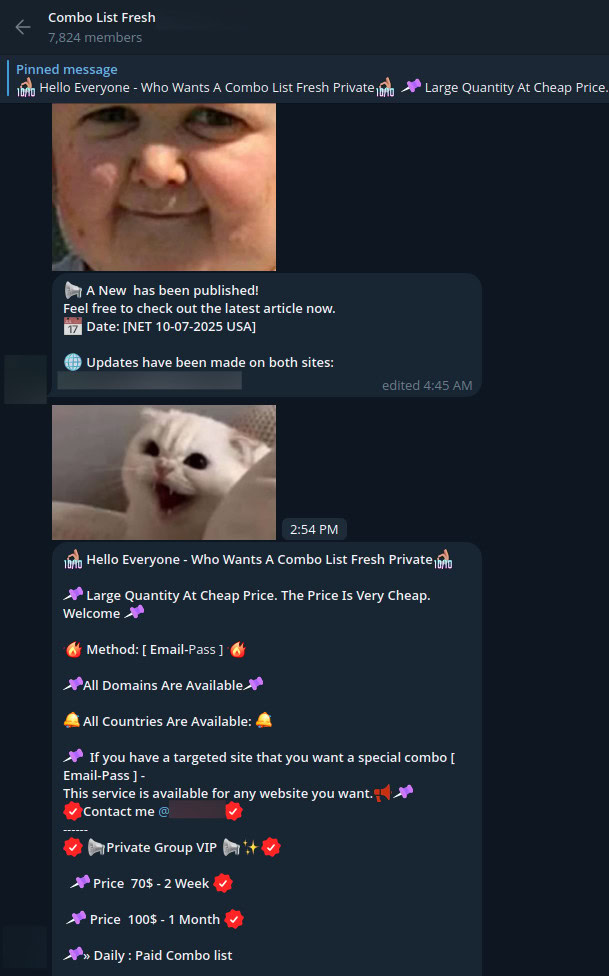
What is the Dark Web’s Role in Combolists?
Threat actors rely on the dark web and cybercriminal communities to buy and sell combolists. The dark web provides the anonymity threat actors need to trade combolists with less risk of arrest.
There are thousands of cybercrime communities, and dark web monitoring ensures that security teams notice relevant targets and are alerted to credential-based threats.
Automatic Credential Stuffing: How Attackers Scale Credential Abuse
Credential stuffing is not a manual process. Threat actors use specialized software to test millions of username and password combinations against target services automatically. The most widely used tools in the cybercrime ecosystem are OpenBullet and its successor, SilverBullet.
How are these Tools Used for Credential Stuffing?
OpenBullet and SilverBullet are credential stuffing frameworks originally marketed for penetration testing. In practice, they have become standard tools for account takeover attacks. The software automates the entire process: loading credentials, rotating through proxies to avoid detection, sending login requests, and logging successful hits.
A single attacker running this software can test hundreds of thousands of credentials per hour against a target service. The tools handle CAPTCHAs, rate limiting, and other defenses automatically when configured correctly.
How Automated Credential Stuffing Works
The tools rely on three components:
- Configs: Custom scripts that tell the tool how to interact with a specific website. A config contains the login URL, form field names, success and failure indicators, and instructions for handling security challenges. Configs are site-specific. A config written for Netflix will not work against Spotify.
- Proxies: Lists of residential or datacenter proxies that rotate with each request. This distributes the attack across thousands of IP addresses, making it difficult for targets to block based on rate limiting or geographic anomalies.
- Wordlists: The combolists containing credentials to test. These are loaded into the tool and processed line by line against the target.
When an attacker runs a stuffing operation, the tool reads a credential pair from the wordlist, selects a proxy, submits the login request according to the config’s instructions, and evaluates the response. Valid credentials are logged as “hits” and exported for use or sale.
The Config Economy
Writing configs requires understanding how a target website handles authentication. This takes time and skill. As a result, a secondary market has emerged where threat actors buy and sell pre-built configs for popular services.
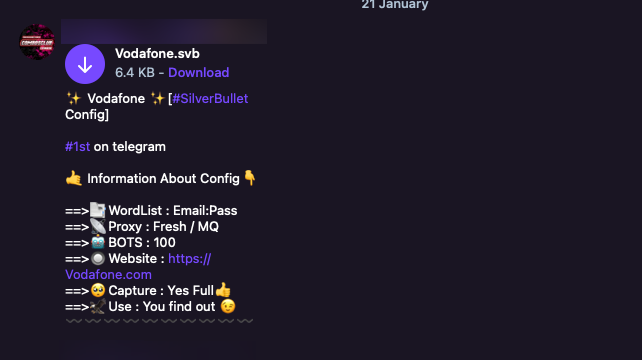
Telegram message advertising configs
Configs for high-value targets like banking portals, corporate SSO providers, and e-commerce platforms command premium prices. Free configs for streaming services and gaming platforms circulate widely on forums and Telegram channels.
When a website updates its login flow, existing configs break. This creates ongoing demand for updated versions, sustaining a cottage industry of config developers who maintain libraries of working scripts.
Targeted Social Engineering Attacks Using Credential Stuffing
Not all credential attacks are automated spray-and-pray operations. In higher-stakes scenarios, threat actors take a more deliberate approach: manually researching specific employees and hunting for their personal credentials to test against enterprise systems.
How Credential Stuffing Attacks Work
The attacker starts by identifying high-value targets within an organization. These are typically employees with elevated access: system administrators, DevOps engineers, finance personnel, or executives. LinkedIn, corporate websites, and conference speaker lists make this reconnaissance straightforward.
Once a target is identified, the attacker searches for personal email addresses associated with that individual. Personal emails are often discoverable through social media profiles, domain registration records, conference registrations, or data broker sites.
With a personal email in hand, the attacker queries breach databases and stealer log repositories for any credentials tied to that address. If the employee used their personal email to sign up for a service that was later breached, those credentials are now in the attacker’s hands.
The final step is testing. The attacker takes passwords from the employee’s personal accounts and tries them against corporate systems: VPN portals, SSO providers, email, cloud consoles. If the employee reused or slightly modified their personal password for work, the attacker gains access.
Why These Attacks Succeed
Password reuse between personal and professional accounts is endemic. Employees who would never share their work password freely may use the same password for their personal Netflix, gym membership, or gaming accounts. When those services are breached, their work credentials are effectively compromised by proxy.
The attack also exploits a gap in most security programs. Enterprise security teams monitor for corporate credential exposure. They check whether company email addresses appear in breach databases. But very few organizations monitor for personal credential exposure of their employees.
This creates a significant blind spot. An attacker who finds a CFO’s personal Gmail credentials in a stealer log can test those credentials against the corporate finance portal. The security team has no visibility into the exposure because it occurred outside the corporate domain.
The Effort and Reward Tradeoff
These attacks require more work than automated stuffing. The attacker must conduct reconnaissance, correlate identities across personal and professional contexts, and manually test credentials. This limits scale.
However, the payoff can be substantial. A single valid credential for the right employee can provide access to sensitive financial systems, source code repositories, or administrative consoles. The precision of the attack also makes it harder to detect. There is no flood of failed login attempts to trigger alerts, just one or two successful authentications that blend into normal traffic.
Organizations with high-value assets, such as financial institutions, technology companies, and critical infrastructure operators, are most likely to face this type of targeted attack.
Closing the Gap
Defending against targeted credential attacks requires expanding the monitoring aperture beyond corporate email domains. Security teams should consider monitoring for personal credential exposure of employees in sensitive roles, enforcing unique passwords through enterprise password managers, and implementing phishing-resistant MFA that cannot be bypassed with a stolen password alone.
Targeted Credential Attacks
When automated stuffing is not enough, threat actors manually hunt for personal credentials of high-value employees to test against enterprise systems.
The blind spot: Most security teams monitor for corporate credential exposure but not personal accounts. An employee’s breached Gmail password can become an enterprise breach if reused at work.
Why Do Combolists Matter in Today’s Cybersecurity Landscape?
Combolists and credential stuffing are the primary vector threat actors use to compromise enterprise accounts in the 2020s. Effectively building a monitoring approach to credential leaks is pivotal to reducing the risk of ransomware and enterprise account takeover attacks. The ease with which threat actors can find credentials has significantly lowered the barrier to entry for criminals, making attacks simple for even very low skill threat actors.
How to Mitigate Risks Arising from Combolists
Protecting your organization from the risks of combolists requires a multi-layered approach across people, processes, and technologies.
Enforce Password Best Practices
Employees are an organization’s first line of defense. Provide employees with cyber awareness training that addresses the key fundamentals of a strong password or passphrase:
- Choose a unique password for each account.
- Avoid using common passwords.
- Use a combination of letters, numbers, and special characters.
Your organization can also set password requirements like a minimum length of 12 characters and periodic mandatory resets.
Provide a Password Manager
According to one report, an employee manages an average of 87 passwords in their workplace – far too many passwords for an employee to remember.
With a password manager, employees can store login credentials securely. They only need to remember one master password to access their other login information.
Password managers make it easier to manage passwords while protecting them from threat actors.
Implement and Enforce Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
MFA provides an additional layer of authentication of logins. It makes sure that employees verify their identity twice. MFA is a combination of two or more of the following:
- Something a person knows (password/passphrase)
- Something a person possesses (token, device)
- Something a person is (biometrics, like a fingerprint or face ID)
Linking a user’s credentials to another identity verification process deters malicious actors. It makes it more difficult to engage in credential-based attacks because bad actors might not get around MFA.
Mitigate Threats from Leaked Credentials with Flare
The Flare Threat Exposure Management solution empowers organizations to proactively detect, prioritize, and mitigate the types of exposures commonly exploited by threat actors. Our platform automatically scans the clear & dark web and prominent threat actor communities 24/7 to discover unknown events, prioritize risks, and deliver actionable intelligence you can use instantly to improve security.
Flare integrates into your security program in 30 minutes and often replaces several SaaS and open source tools. See what external threats are exposed for your organization by signing up for our free trial.