Dark Web Monitoring
Instantly Identify Stolen Credentials, Infected Devices, and Third-Party Data Exposures on the Dark Web
Flare monitors thousands of prominent cybercrime communities across sources as diverse the traditional dark web (Tor), Telegram, and I2P. Our platform automatically collects, analyzes, structures, and contextualizes dark web data to provide our customers with high-value intelligence specific to their organization. Flare sets up and integrates into your existing security program in 30 minutes and can be easily picked up by junior analysts in a matter of minutes.
Try Flare now
Comprehensive Surveillance of Key Dark Web Forums & Markets
Flare helps companies build a threat-led cybersecurity program.
Cybercrime Communities Monitored
Stealer Logs Ingested
Threat Actor Profiles
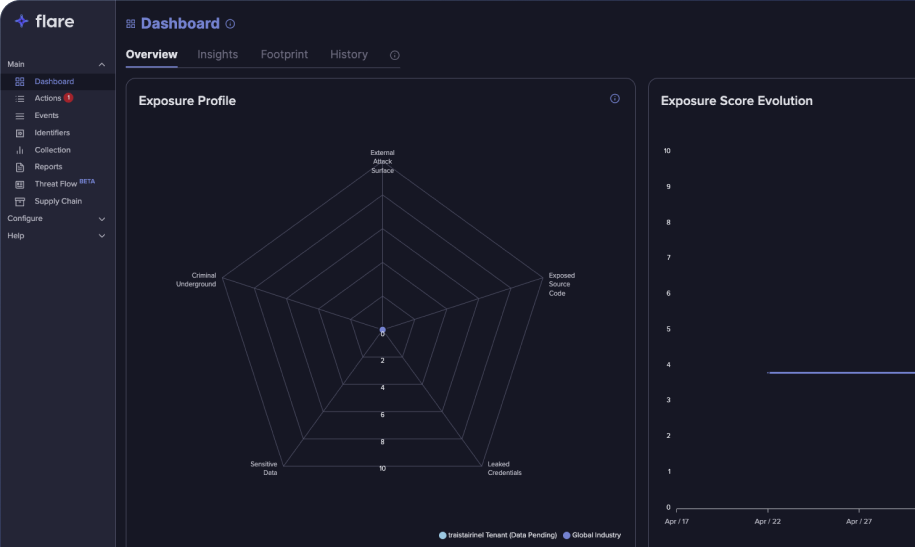
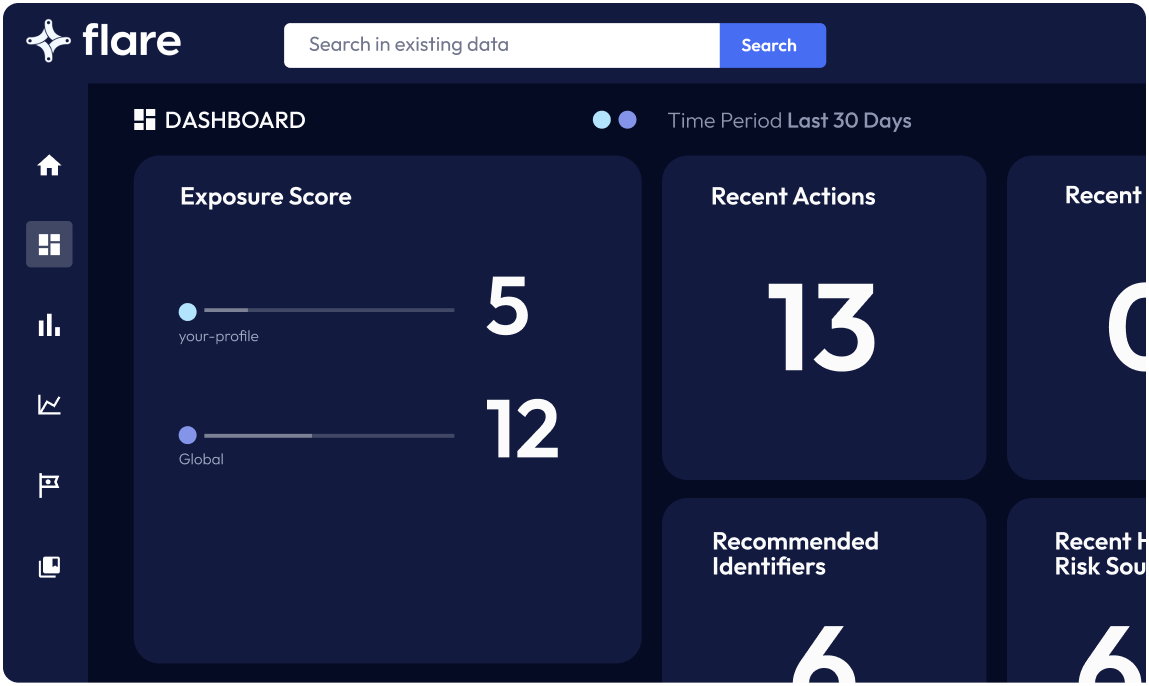
Automate and Scale Threat Detection Across Millions of Dark Web Data Points
Defining Dark Web Monitoring
Experience the Cutting Edge of Dark Web Monitoring Software with Flare
Act Quicker with Tailored Insights
As the attack surface increases, data leaks and breaches have also increased. Currently organizations face coverage issues that prevent them from finding data leaks before they become data breaches.
Better Understand Risks with Threat Actor Analytics
Data leaks can present themselves through multiple avenues. A developer may leave sensitive code on Github, an employee’s credentials may leak from an external breach, or a data leak may surface up on a site like Pastebin. Organizations need proactive continuous monitoring of the different ways your data can leak.
Make Better Informed Decisions with AI Event Contextualization
The more data an organization handles, the higher the chance for it to be exposed by human error. According to a recent IBM Cyber Security Intelligence Index Report, “Human error was a major contributing cause in 95% of all breaches.”
Automated monitoring, identification, contextualization and prioritization of dark web threats can help your analysts focus on what matters most — remediation of digital risks.
Transparency: Core to Flare’s Dark Web Monitoring Approach

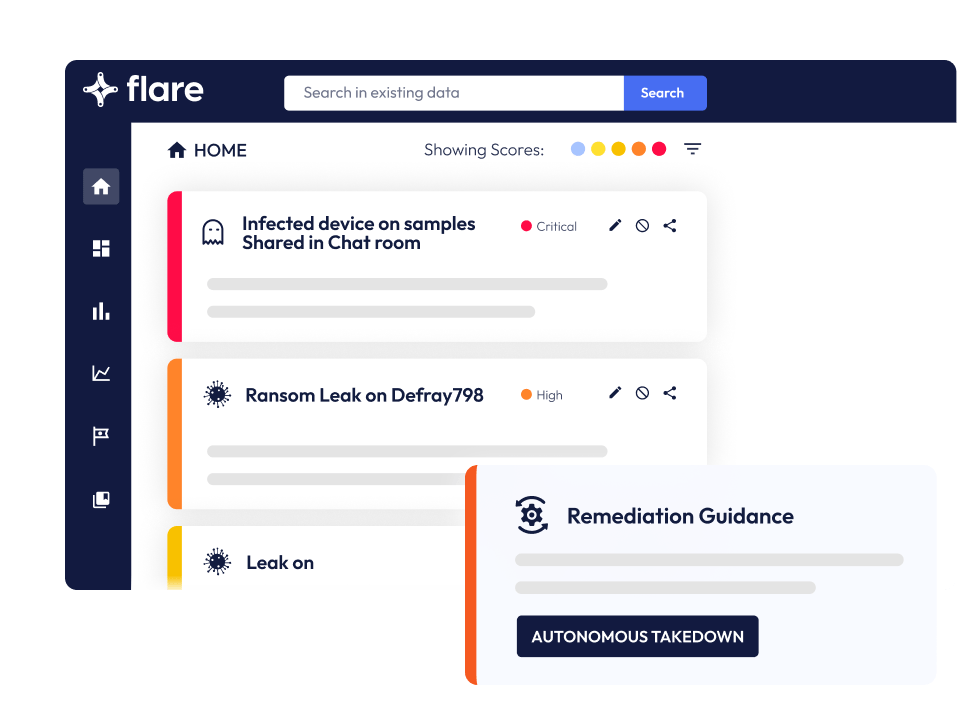
Identify Leaked Credentials
Flare enables you to automatically scan the dark, deep, and clear web for leaked or stolen account credentials. This approach empowers you to proactively identify these credentials for sale on the dark web and prevent data breaches before malicious actors exploit them. Additionally, being aware of employees using their corporate email accounts on external sites allows your organization to proactively remediate and prevent data breaches.
Detect Targeted Threats
Flare generates real-time alerts if your company or assets are mentioned on the dark, deep, or clear web. The platform creates and maintains a dynamic map of your digital footprint, and uses proprietary technology to cache the dark web, providing you with anonymity and allowing you to gather threat intel with far less risk than if you were actively monitoring the dark web yourself.

Prevent Account Takeover Attacks
When a customer creates an account or resets his password, his new credentials are compared in real-time with those stored in Flare. If a match is found, our system will suspect an account takeover attempt and you will be alerted immediately that the credentials are not secure and that he/she should use a different password.

With Flare’s Dark Web
Monitoring You Can:
Decrease dark web investigation time by

Cut data leak incident response costs by

Monitor
Monitor these Illicit
Sources with Flare:
Dark Web/Tor
Flare provides unmatched coverage across TOR sites with 6 years of archived data built into the platform. Customers are empowered to search through our entire data set & continually detect mentions of their name, domain, or organization.
Telegram Cybercrime Channels
Flare covers more than 4,000 cybercrime Telegram channels including those focused on combolists, stealer logs, fraud, and hacking. Our AI Assistant automatically summarizes and translates posts from rooms of interest and analysts can seamlessly pivot between threat actor profiles.
Stealer Logs
Flare’s platform automates collection & detection for stealer log files from dozens of public & hidden Telegram channels in addition to leading dark web marketplaces like Russian & Genesis market. We collect more than a million new stealer logs per week & empower seamless searches through Flare’s easy to use UI.
Customer Success Stories
Check out our case studies to see real life examples of how security teams use Flare to reduce risk.
Verified Reviews
“We audited dozens of different solutions and Flare was the only one making CTI easy and understandable for all, with the right data.”
“What used to take about 1500 hours to complete can now be done in 1 week. Flare allows me to empower junior analysts to do dark web investigations that were previously impossible, hence liberating bandwidth.“
“Other solutions would present us with thousands of potential leaks which were impossible to work with for our small team, Flare was the only one that could successfully filter and prioritize data leaks with their 5-point scoring system.”
“Flare enables us to react quickly when threats are publicized. It helps us protect our brand and financial resources from data breaches.”
Dark Web Monitoring FAQs:
What is the dark web?
The dark web is intentionally hidden and requires the use of special tools like the Tor browser, which enables anonymous communication and browsing.
In contrast, the clear web is the publicly accessible portion of the internet that standard search engines index and search. It consists of websites and resources that are openly available to users without any special access requirements or encryption protocols. The deep web includes all the pages that search engines don’t index including password-protected websites and websites that choose not to be “crawled” by search engines. The deep web contains content that’s stored in databases that support services on the clear web, such as social media platforms or subscription streaming services.
While the dark web hosts various illegal activities, such as the sale of stolen data, drugs, and weapons, it also facilitates other activities, including privacy-focused communication, political activism, and sensitive information sharing in oppressive regimes.
The anonymity provided by the dark web makes it appealing for both legal and illegal purposes, as it allows users to communicate and share information without revealing their identities or locations.
Though threat actors are often associated with the dark web, they gather in many areas across the clear & dark web and illicit Telegram channels. Dark web monitoring is one essential piece of a comprehensive cyber threat intelligence strategy.
What types of information are sold on the dark web?
Here are some common types of data you might find on the dark web:
- Personal/protected health information (PHI)
- Names and birthdays
- Login credentials and security question answers
- Exposed technical data and source codes
- Personally Identifiable Information (PII) such as home addresses
- Financial data, bank accounts, and credit cards
- Software source code
- Company proprietary information
What is dark web monitoring?
Dark web monitoring involves proactively scanning and analyzing the dark web to identify potential threats linked to your organization’s data.
Illicit forums and markets facilitate threat actors in buying and selling stolen data and hacking tools. Their actions generate data points that can then provide your CTI team with actionable intelligence to protect assets.
What are the benefits of dark web monitoring?
Dark web monitoring offers multiple benefits:
- It provides early threat detection.By continually scanning the dark web for your business or personal data, it can alert you to a data breach before it has a chance to escalate.
- It helps protect your reputation. Businesses that are victim to a data breach not only suffer financially but can also lose their customers’ trust. By identifying threats early, you can take action to mitigate the impact and maintain your reputation.
It provides peace of mind.Knowing you have processes in place to monitor your data 24/7 can help reduce anxiety about potential threats so that you know your company’s information won’t be leaked undetected on the dark web.
Is monitoring the dark web necessary?
As organizations become increasingly digitized, cyber threats and data breaches also unfortunately increase. Threat actors can steal organizations’ data or human error and faulty security controls could leak data. Malicious actors can buy and sell this leaked/stolen information. Dark web monitoring is crucial as it helps businesses identify if they have any compromised sensitive data in illicit communities. This allows them to take steps to secure their networks and prevent further damage. They could also detect their sensitive information that ended up on the dark web through a third-party, and could secure their information before receiving official notice of a compromise from that third-party.In 2022, the average amount of time for CTI teams to identify and contain a breach took about 277 days or 9 months. By shortening the time through robust dark web monitoring, organizations can better protect themselves and avoid/decrease costly consequences.
Is dark web monitoring safe?
Yes, dark web monitoring is safe when executed through trusted cybersecurity platforms or with managed security service providers (MSSPs).
They use advanced technology and security protocols to navigate the dark web. They can monitor various illicit communities without jeopardizing their own systems or their clients’ data.
Furthermore, cybersecurity platforms and professionals adhere to ethical guidelines and legal requirements, so they do not engage with illegal activities on the dark web. Their goal is to identify and mitigate potential threats, not to interact with the illicit components of this hidden network.
What are dark web monitoring services?
A dark web monitoring service is a cybersecurity solution offered by specialized firms. It involves scanning the dark web for data related to a specific organization or individual within that organization. This could include personally identifiable information (PII), credit card details, login credentials, or sensitive company information. If the service detects such data, it alerts the client, enabling them to take remedial action.
What is dark web monitoring software?
Dark web monitoring software is a tool that can scan, identify, analyze, and report activities on the dark web that are relevant to your organization. Since this part of the internet is not indexed by standard search engines, threat actors often use it for illicit activities including buying and selling stolen sensitive information.
Dark web monitoring software can makes monitoring easier as individuals do not have to manually search through each dark web source. Therefore, using this tool can enable organizations and security operations teams to act quicker with mitigating potential risks.
How do I monitor the dark web?
What is dark web credential monitoring?
Does my organization need dark web monitoring?
Considering the rise in data breaches, cybersecurity threats, and the value of data in today’s digital economy, proactive monitoring provides an essential layer of protection.
Dark web monitoring is a valuable measure in protecting your organization against cyber threats. A monitoring service or platform can support your CTI team in staying one step ahead of potential threats and cybercriminals’ evolving tactics.
What’s the benefit of automating dark web monitoring?
Manually searching through the dark web is one possible way of monitoring, but it is inefficient, prone to missing items, and emotionally/mentally exhausting. Automated monitoring tools can accurately and continuously scan illicit communities much more comprehensively than is possible with manual methods. Automated dark web monitoring enables reliable surveillance and also significantly faster response times to mitigate threats (with prioritized alerts).
In addition, automated dark web monitoring can make gathering dark web analytics easier, so that security teams can benefit from cleaned and structured information about the dark web that is relevant to their organization.
Can I automate searching through dark web search engines?
Flare is not a dark web search engine, but tracks dark web forums and markets (as well as illicit Telegram channels), so your security team can safely monitor these sources in the platform without manually searching for them.
Does dark web monitoring include dark web scraping?
Dark web scraping tools typically can have hidden expenses such as requiring specialized skills or being time-consuming.
Flare addresses dark web scraping needs by automating time-consuming, manual dark web monitoring tasks.
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.
Learn More About Proactive Dark Web Monitoring
Don’t stay in the dark. Read more in these resources: