While readily available, malware is far from being the only tool that malicious actors use to steal data and illegally access computer networks. Malicious actors indeed threaten firms’ security using far more mundane and everyday techniques.
Case in point: taking advantage of Google, the world’s most popular search engine, to find confidential information and vulnerabilities in your firms’ systems. In this blog post, we explain how malicious actors conduct reconnaissance on your systems without ever touching them. We also cover what their main reconnaissance targets are and why reproducing the same reconnaissance on your own systems is both a complement to your security solutions and a precious safeguard against exploitation.

What is Google Dorking
Google’s goal is to index the world’s information. While doing so, its indexing robots collect vast amounts of confidential data that were never meant to be opened and public in the first place. With the right search operators, anyone can target that confidential data specifically and find information that was meant to remain private.
Examples of operators
intitle:XXX searches for content in the title of a webpage
filetype:XXX searches for specific file typeA search for intitle:password AND filetype:xlsx would find for example all Excel spreadsheet that have the word password in their title.
This technique, known as “Google dorking” or “Google hacking” is not new. In fact, malicious actors used to be able to search the first several digits of a credit card and find dozens of results for leaked credit card numbers. With the right keywords – also known as “dorks”, a malicious actor can find insecure sensitive information with ease.
The reason for Google Dorking
The first step of a successful attack against a company is reconnaissance. It consists of gathering information on a target actively and passively.
Active reconnaissance refers to actions that security teams are likely to detect such as probing a network. This gives the target an early warning sign that an attack may be coming.
Passive reconnaissance refers to actions that security teams cannot detect. Google dorking is only known to Google who does not detect the dorks nor warn the companies that are targeted using this technique.
Google dorking therefore provides a method for malicious actors to conduct reconnaissance without warning their target they are coming. This increases their odds of success and limits the ability of companies to prepare for an attack.
What do Google Dorks look like
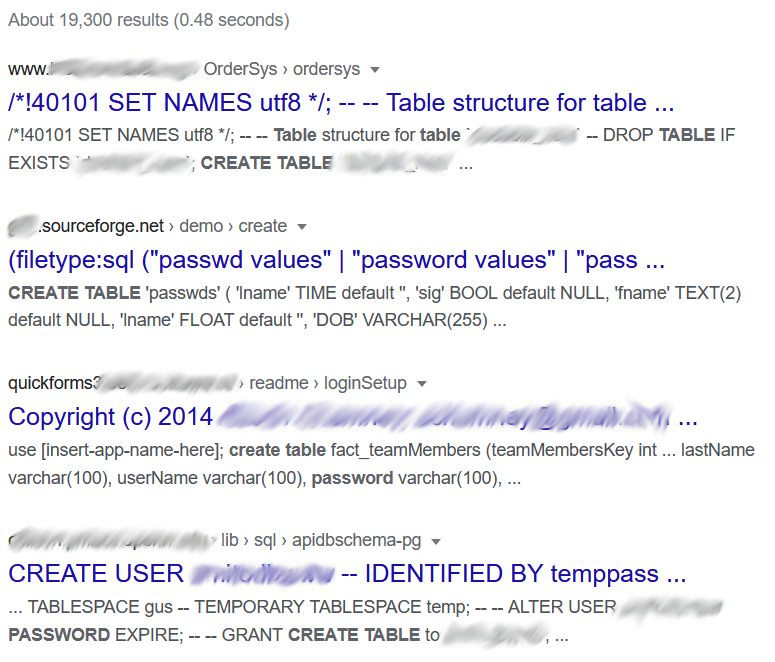
Export files of databases follow a known specific pattern. In the example below, we found files that contain both the data structure of databases as well as all their data. This type of files is used to export data and make backups and should never be published online. These databases are likely to contain thousands of records of individuals with their sensitive personal information.
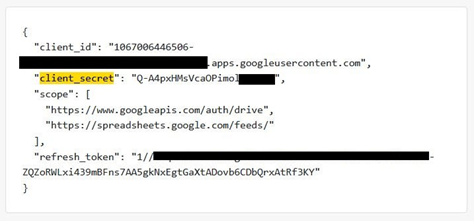
API keys are passwords that grant access to servers and data to anyone who has a copy of them. With access to these keys, a malicious actor can steal, alter or inject data to cloud-based systems. Each online service has its own API key format that can be searched for. In the example below, we found the API keys that control a Google Drive account. Using these keys, it would be possible to access and modify the content located in that Google Drive account.
Finally, malicious actors can find administrative panels to website backends using Google Dorks. These panels may not be protected against password guessing and other types of attacks that lead to website takeover.
Malicious actors share and exchange Google Dorks with each other on numerous online forums. The example below presents how actors share dorks including what the dork itself is as well as what it does. In this case, it lists vulnerabilities for a specific WordPress plugin.
Adopting the malicious actors’ point of view
Malicious actors should not be the only ones running Google dorks to conduct reconnaissance on your computer network. Indeed, if you are to prevent attacks, using the same methods and techniques that malicious actors use allows you to know where you are vulnerable and to gain insights into what malicious actors see and know.
Updating and assessing the vulnerabilities of your computer system is an important part of your security teams’ daily activities. Many companies, however, conduct penetration tests regularly to identify systems that are vulnerable and in need of patching. Using Google Dorks fills in a similar role in your security processes. It serves as an insurance when your security systems have not detected a public vulnerability.
Building and updating a list of Google Dorks requires a specific expertise that solution providers such as Flare Systems offer. We constantly update the list of Google Dorks that we run using our customers’ names and key resources. Our infrastructure runs a scan every hour against all the dorks we have implemented and alerts in real-time our customers, providing industry-leading automation. This enables us to detect any information leakage before malicious actors can and to help our customers take down the information. Interested in doing some further reading? Take a look at our blogs on the Safepay Ransomware Group and Top Threat Intelligence vendors of 2026.