Generative artificial intelligence (AI) and large language models (LLM) dominate current technology conversations. From ChatGPT to DALLE 2, generative AI has become the new hype technology overtaking the corporate world. With all the hype around generative AI, the idea that it is a tool that can enable rather than replace people can get lost.
According to recent research, global cybersecurity job vacancies grew by 350% with the current number of unfulfilled jobs at 3.5 million. Beyond unfulfilled roles, companies struggle to balance their cybersecurity needs with the limited experience that someone new to the field has.
With Flare’s AI Powered Assistant, CTI teams can benefit from enhanced automated exposure monitoring. These capabilities include Threat Actor Profiling, which analyzes a threat actor’s complete post history in seconds and generates a detailed summary of that threat actor’s TTPs.
The Clear and Dark Web Convergence
Companies today need to worry about several different types of data exfiltration and exposure across corporate, employee, and customer information.
For example, think of the various ways that companies leak data:
- An employee uses an unauthorized service without realizing that the data isn’t secure, making information publicly available.
- A public service, like GitHub, is misconfigured, leaking hardcoded secrets.
- A third-party vendor experiences a data breach.
- Malicious actors deploy an attack to collect data so they can sell it.
In the past, malicious actors used the dark web because it was anonymous, enabling them to hide their illegal activities. Today, the clear web offers this same anonymity due to the sheer volume of available services. Often, modern malicious actors choose to hide “in plain sight,” using various legal digital services like:
- Illicit Telegram groups
- Discord servers
- Google Drive/Dropbox
For example, a Telegram post will link to a service with a different capability, like a Discord server that allows screen sharing. Tracing the activity further, the Discord server may send you to a Tor site.
Generating Threat Actor Profiling with Flare
As activities across the clear, deep, and dark web become more intertwined, tracking threat actors becomes more challenging. A threat actor can use multiple personas or handles, both on a single service or across multiple services.
Flare’s machine learning models and natural language processing (NLP) create context that detect cybercriminals as they move across various platforms. Our data science team has been using machine learning and other forms of AI for the past several years to analyze data, prioritize events, recommend actions, and make predictions. Now, we’re translating that into helping you uncover patterns and relationships between otherwise disconnected threat actors using data like:
- Speech patterns
- Word choice
- Abbreviations
- Slang
- Post telemetry
We combined a generative AI model, our NLP, and the archived dark web data that we collected over the past six years. With this information, we generated two million threat actors profiles, eliminating manual monitoring and reducing the need for highly skilled analysts. At the same time, these profiles give the highly skilled analysts technical information they can use when trying to prioritize their activities.
For example, by using NLP and Threat Actor Profiling, an organization currently tracking 200 threat actors may learn that only 50 of those threat actors are actually the same person or group. This provides several advantages:
- Visibility into a more targeted threat
- Context about different activities
- Aggregating handles or personas into a single group for better monitoring
- Reviewing activity volume and activities to tie different names and locations together
- Leveraging predictive analytics to identify potential likely next steps
Use Cases for Threat Actor Profiles
Threat Actor Profiling gives you a way to identify and add context to your threat intelligence research without requiring advanced or platform-specific skills.
Correlating Across Time and Place
With NLP and Flare’s archives, you can identify similarities across various communication services to look for targeted threats.
Flare’s Threat Actor Profiling uses generative AI to identify similarities across the different locations and times to give you insights about the threat actors. For example, in this profile, the threat actor(s) appear to focus on:
- Gaining unauthorized access to Remote Desktop Protocol systems
- Targeting chemicals, financial, lighting products, telecommunications, and blockchain development

Comparing Across Personas and Handles
To evade detection, threat actors change their online “identities” by using different names or hiding their IP addresses. Combining Flare’s archived data and NLP models, you can identify a threat actor’s use of words and context based on the person’s writing style and online “voice.”
In the example below, you can see how Flare’s Threat Actor Profiling compares these data points across twelve sources for a threat actor using two usernames, one beginning with a C, the other with an S.
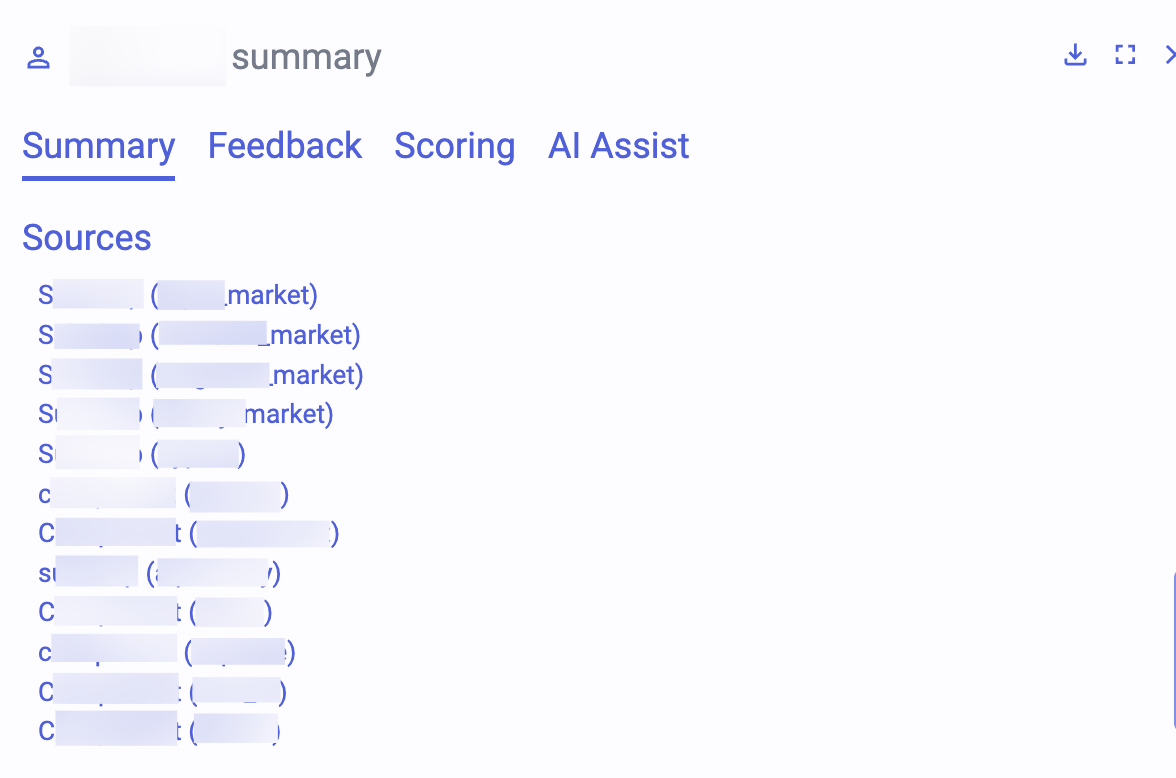
Unlike people, AI models can rapidly analyze large data sets to find these small similarities that create patterns. By leveraging generative AI and NLP, organizations gain visibility across these otherwise seemingly unconnected accounts and services.
Identifying Reuse
While malicious actors may work together, they’re not loyal to one another. Often, you’ll see almost complete code swipes where one malware is 95% similar to another with a different name. Similarly, you see the same thing with traded techniques.
The Future of AI and Cyber Threat Intelligence
By the numbers and statistics, a majority of data leakage comes from employees and vendors. However, these accidental data exposures are typically a lower risk that the data exposures associated with threat actors. When threat actors steal data, they have a malicious intent that’s almost always financially motivated.
Despite some recent hacktivism and distributed denial of service (DDoS) attacks arising from it, money and data will likely remain the primary reason that malicious actors target organizations. People – and organizations – need to shift their expectations and assume that they have some data exposed. Statistically, most large organizations with mature programs understand that security controls have been bypassed, so they implement programs that enable them to detect and remediate it quickly.
By leveraging generative AI and LLM, organizations can monitor their digital footprints more effectively so that attackers no longer have the information advantage.
Leveraging AI for CTI with Flare
Malicious actors are already imagining and trying out cybercrime strategies involving generative AI as seen in the examples above. However, LLM tools are a testament to human ingenuity and the immense positive potential of AI. It’s our collective responsibility to ensure that these capabilities are for our collective benefit, and not to the detriment of the digital landscape.
Our approach at Flare is to embrace generative AI and its possibilities, and evolve along with it to provide cyber teams with the advantage. LLMs can be incorporated into cyber threat intelligence to be an essential capability to more rapidly and accurately assess threats.
Sign up for a free trial to learn more about what Flare’s AI Powered Assistant can do for you.