
Threat actors deploy many tactics, techniques and procedures (TTPs) to get access to sensitive data assets. Among this arsenal of weapons, obtaining correct user credentials (username and password pairs) that can be used for credential stuffing attacks plays a central role in most data breaches.
Poor password hygiene makes some credentials easy to guess. Social engineering tactics can dupe users into disclosing their passwords using convincing pretexts. But arguably an even easier and more accessible method of getting the veritable keys to the kingdom of data is by using one of the billions of leaked credentials circulating on the dark web.
The proliferation of leaked credentials on this somewhat hidden corner of the internet poses challenges in data breach prevention. Identifying leaked credentials on the dark web and resetting affected user accounts is critical to stopping many data breaches from occurring. This article offers some tips and approaches for finding leaked credentials on the dark web belonging to an employee or contractor with access to your company’s data. Proactively identifying users with compromised conditions can enable you to effectively reduce the risk of being breached.
A Quick Refresh on What the Dark Web Is
The dark web is an area of the internet that provides encrypted,anonymized communications using the TOR network. What appears on the dark web is invisible to normal (clear web) search engines like Google.
Special web browsers are required to access sites on the dark web, which have .onion as their top-level domain. The word onion refers to the layers of encryption that protect the confidentiality of messages and the layers of different nodes that messages pass through to preserve their anonymity.
While there are legitimate reasons to use the dark web (e.g. journalists in oppressive regimes wanting to preserve their privacy), the available anonymity primes it as a hub for illicit cyber activity. Forums, social media sites, and marketplaces provide platforms for cybercriminals to discuss tactics and exchange stolen data for a fee. Often, the data traded on the dark web comes in the form of stolen login credentials that could provide buyers with access to services and resources on your network.
The latest estimates revealed there are roughly 10 billion sets of username-password credentials circulating on the dark web.
Data Breach Prevention & The Dark Web
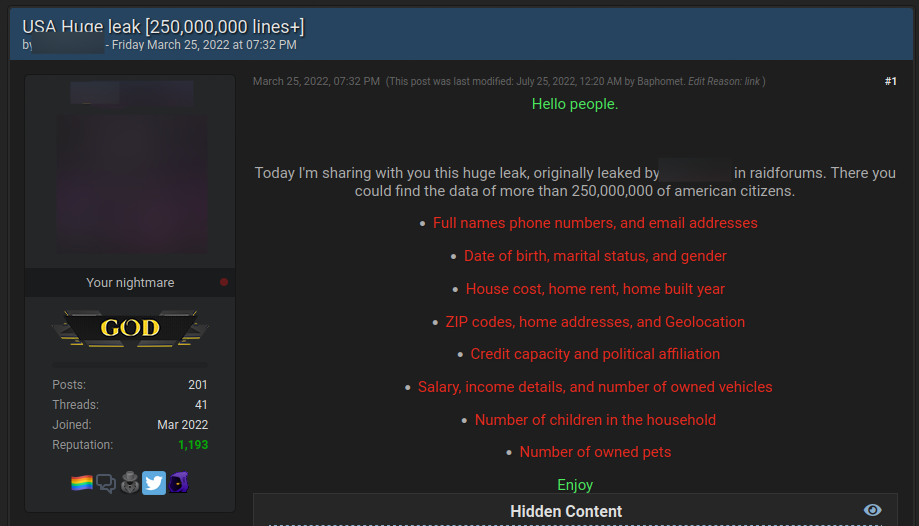
Given the volume of leaked credentials on the dark web, this is a source of risk that doesn’t get the attention it deserves from companies. But why exactly should companies put more emphasis on monitoring sites on the dark web for leaked credentials? There are two main reasons, and they both relate to data breaches.
1) Preventing Data Breaches using Dark Web Data
Over 60% of data breaches begin with stolen credentials as the initial access vector. This might sound like it somewhat simplifies how data breaches happen. It’s not that obtaining someone’s credentials automatically provides sensitive data access.
Integrate the world’s easiest to use and most comprehensive cybercrime database into your security program in 30 minutes.
But it’s crucial to remember that skilled hackers have a range of offensive cybersecurity techniques at their disposal. Once inside your environment, even with a non-privileged user account, hackers can extract information about users and progress deeper through lateral movement, privilege escalation, or other exploits.
As a case in point, the infamous Colonial Pipeline breach of 2021 originated from using stolen credentials to access a corporate VPN account. Monitoring the dark web for leaked employee credentials is a useful method for proactively detecting potential high-risk exposure that can be remediated before it becomes a data breach.
2) Detecting Data Breaches on the Dark Web
Across all industries, it takes companies an average of over six months to discover that a data breach has occurred. While attacks like double extortion ransomware could quickly flag a breach of company data, most hackers don’t openly broadcast it to companies when they’ve exfiltrated information from their networks.
Shortening the time to detect data breaches is another compelling reason to monitor the dark web for leaked credentials. This is especially important for companies with customer-facing online services where stolen credentials could provide access to customer accounts and facilitate fraud.
While you might argue that by the time credentials have been leaked on the dark web, the damage is already done, that’s not the case. A nefarious actor still needs to purchase these credentials and use them. If you can detect breached and leaked credentials faster by monitoring the dark web, you can take actions such as resetting affected accounts en masse to reduce the damage. Your company’s reputation may depend on how quickly you detect and respond to data breaches.
How to Effectively Use the Dark Web to Prevent Data Breaches
Some surprising research from 2022 found that 62% of security professionals lack the tools and training required to detect their organization’s data on the dark web. Two approaches commonly used are manual and automatic monitoring.
- Manual dark web monitoring tasks security teams with manually trawling through relevant dark web forums and marketplaces for leaked credentials and other data. This approach is incredibly resource-intensive given the volume of different sites and information on the dark web. Security teams, already stretched by other important tasks, are unlikely to have the time to manually monitor the dark web with any degree of coverage. Furthermore, sorting through the noise to uncover useful data increases the workload. And all of this doesn’t even account for the fact that many security professionals have never even browsed the dark web.
- Automated dark web monitoring uses tools to automatically scan the dark web for leaked credentials and other relevant information about your company. Advanced tools leverage the latest developments in the disciplines of artificial intelligence, machine learning, data mining, and natural language processing to identify credentials for sale on the dark web.
The ideal approach is to use an automated solution as the basis for dark web monitoring and combine this with the experience and knowledge of security teams who can manually add specific marketplaces, Telegram channels, or other areas to monitor.
Data Breach Prevention with Flare
Flare’s platform, powered by an AI-driven data collection system, automates dark web monitoring and provides real-time alerts to detect leaked credentials. Flare saves your company time and money by sifting through noisy data while providing complete coverage across the dark web for data breach prevention and detection. You can also tweak the platform to suit your organization’s needs to search through preferred sources of cyber risk where credentials are most likely to end up.


