
Executive Summary
- Over the past few months we’ve focused and highlighted various threats across illicit sources in these Threat Spotlights
- We’ve collected a few of them them here as 12 Days of Threats to celebrate the holiday spirit
- Strong threat monitoring strategies are holistic and consider these top threats, and others
1. Russian Market (Infected Devices & the Growing Threat of Stealer Malware)

Infected device markets sell access to infected computers and browser fingerprints that can be used by threat actors to compromise online accounts. Like identity theft, the infected device can reveal a wealth of personal information about the victim, like where they live, their job, their hobbies, and even local venues like gyms that they frequent. The Russian Market is a dark web autoshop with about 2.7 million logs for sale for about $10 each. The market averages about 40,000 new bots for sale per week.
2. Genesis Market (Infected Devices & the Growing Threat of Stealer Malware)

Much like the Russian Market mentioned above, the Genesis Market sells infected devices containing an abundance of the victim’s personal information and login credentials. Launched in late 2018, Genesis Market is a clear web autoshop with about 400,000 bots for sale. Genesis averages about 1,600 new bots for sale per week. The stealer logs range in cost from about less than a dollar to a little over $170.
3. TOR (Illicit Telegram Markets & OTP Bots)

The TOR browser allows for nearly completely anonymized browsing. Threat actors are moving off of this browser given the incredibly slow speeds (large file uploads and downloads can take days or weeks) and permanence of published information (as security companies and government agencies around the world monitor and archive illicit communities). So where are they going?
4. Telegram Markets (Illicit Telegram Markets & OTP Bots)

TOR used to be the go-to area for malicious actors and illicit communities, but they’re moving to different platforms to prioritize speed and greater “anonymity.” Instant messaging channels like Telegram and Discord are:
- Easy to use: It’s faster and more reliable than TOR.
- Have less permanent interactions: Only people on the member list can see the messages and there’s a sense of it disappearing with the flow of new messages. Channels can automatically delete data after a certain time, and if law enforcement and security organizations infiltrate a channel, creating a new channel instantly is simple.
5. OTP Bots (Illicit Telegram Markets & OTP Bots)

Through one time password (OTP) bots, threat actors attempt to gather 2FA codes on a large scale. They are designed and sold with specific companies in mind. For example, if a malicious actor already has the login credentials to a certain account or corporate IT environment, they can buy an OTP bot. Then this bot sends the victim a phishing voicemail or text to ask them for their 2FA code. OTP bots are typically employed for financial fraud on personal bank accounts, but corporate attacks are another application of this technique.
6. Leaked Credentials and Organization Size (Leaked Credentials)

Across almost all industries, the ratio of leaked credentials per employees decreases as the size of the organization increases. This is most likely because of security maturity improvements as the organization becomes bigger. Across all industries and organization sizes, there was an average of 22% of employees that had leaked credentials on the dark web. To break this down, on average, mid-sized companies (500-1,000 employees) had 43% of employees with leaked credentials on the dark web, 19% of employees at large companies (1,000-5,000 employees), and 4% of employees at enterprise companies (>5,000 employees).
7. Leaked Credentials and Industry (Leaked Credentials)

Across the industries of Manufacturing, Software, Energy, Retail, Finance, Healthcare, Food & Beverage, and Labs & Pharmaceuticals, Manufacturing has the highest ratio of stolen credentials for sale on the dark web, while Labs & Pharmaceuticals has the lowest. We weren’t surprised that Energy, Retail, and Manufacturing were in the top four for the highest proportion of leaked credentials per employee. According to Gartner, those industries have a lower ratio of security spend when compared to industries such as Healthcare and Financial Services. However, we were surprised that the Software industry ranked second for the average ratio of leaks per employee, because according to Gartner, “Software Publishing and Internet Services had the highest security spend expressed as a percentage of total information technology budget. And generally, we found that the higher level of security maturity for an organization (measured by number of employees and industry security expenditure) correlated with less leaked credentials.
Integrate the world’s easiest to use and most comprehensive cybercrime database into your security program in 30 minutes.
8. Leaked Credentials and Geography (Leaked Credentials and Geography)
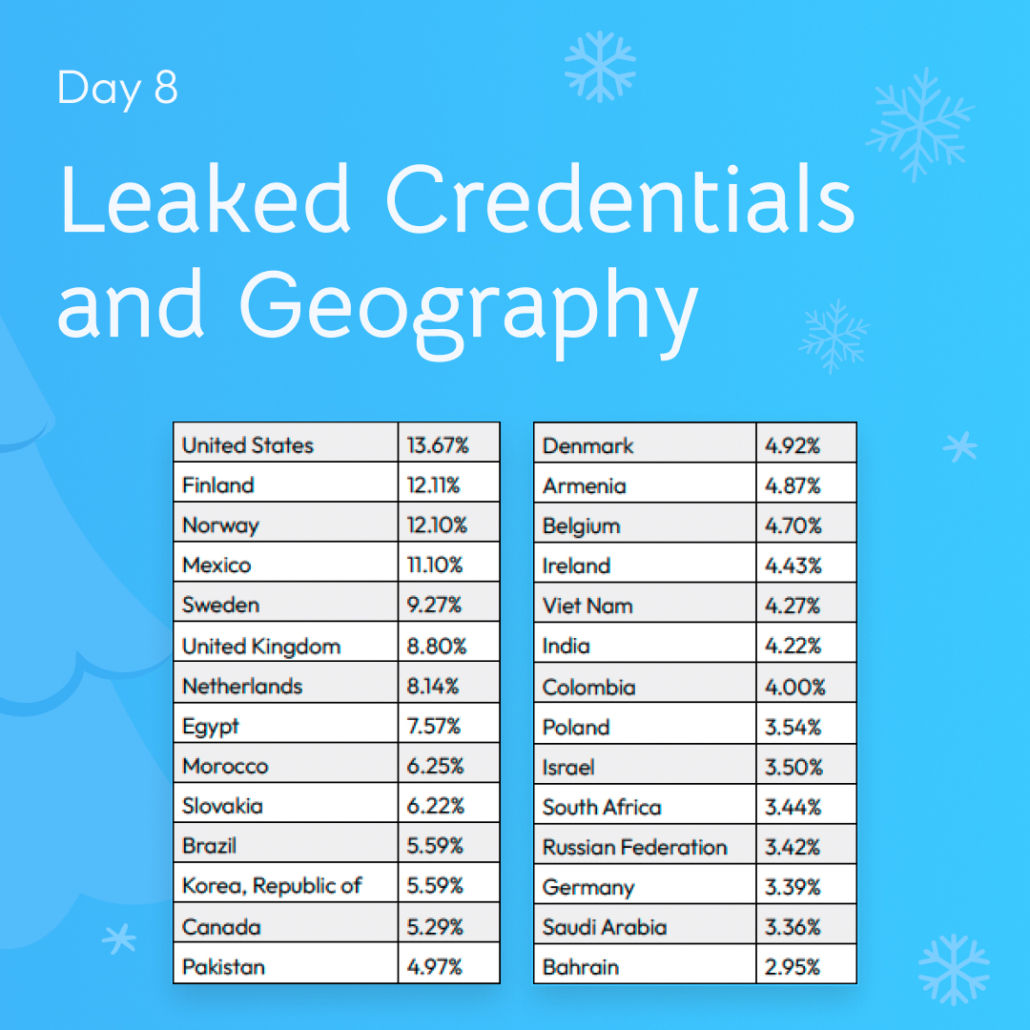
Out of the countries in the world, we looked at the top 28 countries with the average ratio of leaked credentials per employee. The U.S. and Nordic countries ranked in the top 5 for leaked credentials per employee (excluding outliers like Mexico), while countries that spend far less on cybersecurity both nominally and as a percentage of GDP came in lower.
The U.S., Norway, Sweden, and the U.K. are home to several multinational conglomerates worth hundreds of billions of dollars, which contribute to making them targets to threat actors.
9. Big Changes Across Dark Web Marketplaces (Key Trends in Illicit Communities)

The dark web had some significant changes in 2021 and early 2022. The Raid forum takedown and Darkode exit scam (one of the biggest markets of the time) shifted threat actors to different areas. AlphaBay reemerged as a leader.
After all these changes, the dark web marketplace ecosystem is relatively stable for the first time in a while.
10. Ransomware as a Service (Key Trends in Illicit Communities)

Ransomware has become much easier to use and its use has expanded dramatically.
Authorities continuously play “whack-a-mole” by busting ransomware groups that soon are replaced by other groups.
Ransomware gangs are becoming more sophisticated by applying the software as a service model, so threat actors will most likely continue to increase using these in the coming year.
11. Flawed Cybersecurity Mindset (Cyber Warfare & Security in the 21st Century)

This isn’t a traditional “threat,” but if everyone on a company board is not well-versed in cybersecurity, that leaves room for organizational weaknesses. Company leadership must be vigilant about threat actors continuously evolving.
It’s the norm that company leaders can ask questions about financial audits, and this should be applied to cybersecurity as well.
Requiring every company leader to be well-versed about cybersecurity is a more solid approach than relying on one CISO/CIO/another individual well-versed in cyber.
12. Dark Web Data Leaks (Dark Web Data Breaches)

There are 10 billion stolen credentials on the dark web. Many of these login credentials are sold for only a few dollars, but they can lead to disastrous data breaches for people and organizations that cost thousands, even millions of dollars.
How Flare Can Help
Flare enables you to automatically scan the clear & dark web for your organization’s leaked data, whether it be infected devices, technical data, source code, leaked credentials, or secrets on public GitHub repos. This approach enables you to proactively identify sensitive data leaks and prevent data breaches before malicious actors utilize them.
Flare allows you and your security team to:
- Get ahead of reacting to attempted network intrusions before they happen by rapidly detecting stolen credentials and infected devices for sale
- Cut incident response time by up to 95% and monitor around 10 billion leaked credentials
- Understand your organization’s external data exposure (digital footprint) with proactive recommendations to improve your security posture based on real world, contextualized data
Want to see how Flare can help your organization stay ahead of these threats and more? Request a demo to learn more.


